In the fast-paced world of business, financial clarity is essential. Understanding how to prepare a budget and forecast equips companies to make informed decisions, manage cash flow, and achieve growth targets. Think of it as plotting a road trip: the budget forecast sets your route, while forecasts provide real-time updates to adjust for unexpected detours.
Businesses that combine planning, historical insights, and predictive tools are far more likely to succeed in uncertain markets.
Table of Contents
What Is Planning, Budgeting, and Forecasting?
The budgeting and forecasting process is a structured way for businesses to map short- and long-term financial goals.
1. Planning Process
Planning provides the framework for short and long-term financial objectives, typically spanning 3–5 years. It defines the company’s financial strategy, sets financial objectives, and aligns all departments with the overall business goals.
Analogy: Planning is like designing a blueprint before building a house; it prevents costly mistakes and ensures alignment with the final vision.
2. Budgeting
Budgeting details how the plan will be executed month to month. This includes revenue and expense projections, debt management, and cash flow tracking. Companies often prepare an annual budget and adjust based on actual results.
Mini Case Study: A mid-sized service company discovered seasonal dips in demand. By adjusting their budget forecast mid-year, they maintained positive cash flow and optimized resource allocation.
3. Forecasting
Forecasting uses historical financial data and current market conditions to predict future outcomes. Forecasts may include revenue, costs, or headcount, and are updated frequently to ensure relevance.
Life Lesson: Forecasting is like sailing with a compass—you may not control the wind, but you can adjust your sails to stay on course.
Why Businesses Need a Budget and Forecast
- Ensures alignment with financial objectives.
- Improves forecast accuracy and supports better financial decisions.
- Facilitates scenario planning, allowing businesses to prepare for market shifts.
- Enables integrated business planning by connecting sales, operations, and finance.
Statistics: Companies leveraging budgeting and forecasting tools report 20% better financial performance than those relying on manual spreadsheets.
Step-by-Step: How to Prepare a Budget and Forecast
Step 1: Gather Inputs
- Collect historical financial data, current expenses, and expected revenue streams.
- Engage stakeholders to capture insights across departments.
Step 2: Analyze Historical Data
- Review financial statements like balance sheet and income statement.
- Identify patterns in cash flow, seasonal trends, and cost drivers.
| Month | Revenue ($) | Expenses ($) | Net Profit ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | 50,000 | 35,000 | 15,000 |
| Feb | 55,000 | 38,000 | 17,000 |
| Mar | 48,000 | 33,000 | 15,000 |
Step 3: Build Your Budget
- Decide on fixed and variable costs, allocate resources, and define financial goals.
- Use Microsoft Excel or excel spreadsheets for a structured approach.
Step 4: Forecasting Tools and Techniques
- Apply forecasting tools and budgeting software to enhance accuracy.
- Consider qualitative forecasting and predictive models for better projections.
- Use rolling forecasts to continuously update assumptions.
Step 5: Scenario Planning
- Plan for multiple scenarios: best-case, base-case, and worst-case.
- Helps companies react to market shifts and manage risk.
Step 6: Review and Monitor
- Track forecast accuracy against actual results.
- Use FP&A insights for informed decision-making.
- Adjust budgets and forecasts regularly to streamline operations.
Key Concepts and Comparisons
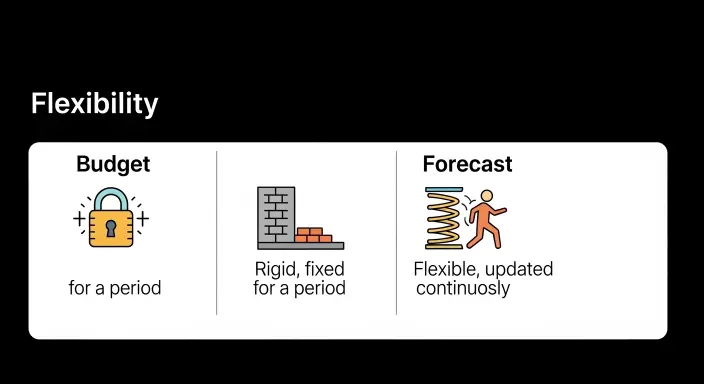
Budgeting vs Forecasting
| Aspect | Budget | Forecast |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Plan revenue and expenses | Predict actual outcomes |
| Flexibility | Fixed, adjusted occasionally | Updated frequently |
| Focus | Resource allocation | Performance and adjustments |
| Timeframe | Annual, monthly | Rolling, quarterly |
Key Differences Between Budgeting and Forecasting
- Budgets are plans and budgets for allocation.
- Forecasts predict future results based on data.
- Forecasting leverages historical data for improved financial performance.
Practical Tips for Businesses
- Build a Budget Carefully: Involve the finance team and departmental heads.
- Leverage Technology: Use budgeting and forecasting software to automate calculations.
- Monitor Regularly: Frequent updates improve forecast accuracy.
- Scenario Planning: Prepare for unexpected changes using multiple scenarios.
- Track KPIs: Net profit margin, cash flow, and revenue growth rate are essential indicators.
Conclusion
Mastering how to prepare a budget and forecast allows businesses to navigate uncertainties, make confident decisions, and achieve sustainable growth. A well-prepared budget forecast is both a roadmap and a compass, guiding organizations toward their financial objectives.
Motivational CTA: Begin today—analyze data, build your budget, forecast future results, and empower your business to thrive.
FAQs
How is a budget different from a forecast?
A budget defines planned allocations for a period, while a forecast predicts actual outcomes using historical data and market trends.
What tools help prepare a budget and forecast?
Budgeting and forecasting tools, Microsoft Excel, and forecasting software improve accuracy, efficiency, and reporting.
How often should forecasts be updated?
Forecasts should be reviewed quarterly or with major changes in market conditions to maintain forecast accuracy.
Who manages the budgeting and forecasting process?
The chief financial officer and finance team lead the budgeting and forecasting process, often collaborating with all departments.
Why is scenario planning important?
Scenario planning prepares businesses for market shifts, mitigates risk, and improves decision-making during uncertain times.

