Every successful business knows that numbers tell stories. Those stories come to life through two essential tools — Financial Budgeting and Forecasting. While both sound similar, understanding the difference between budget and forecast is the key to steering any company toward stability and growth.
Think of it this way: a budget is your roadmap, while a forecast is your GPS — constantly updating your route as conditions change. Together, they help organizations plan for the future, anticipate risks, and make data-driven financial decisions that improve performance and confidence.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Core Concepts

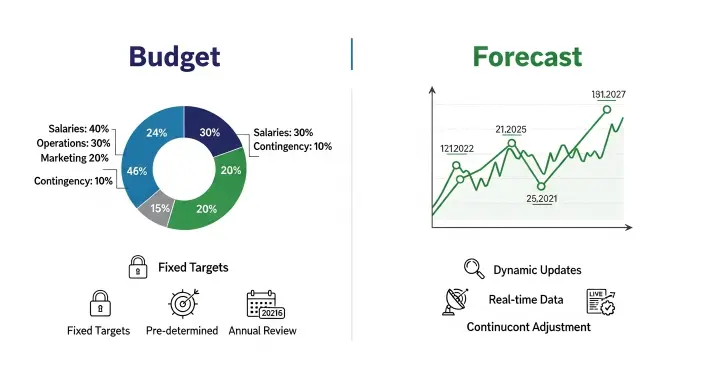
What Is a Budget?
A budget outlines your expected revenue and expenses over a period, usually a fiscal year. It’s based on historical data and forms a financial roadmap that guides resource allocation, spending limits, and targets.
For example, a company may create a budget of $5 million in revenue and $3 million in costs, leaving room for expansion. These figures are outlined in the budget and rarely change unless major events occur. It represents what you hope will happen — not what will happen.
This is why Financial Budgeting and Forecasting is so crucial — it connects your budgeting with real-time insights.
What Is a Forecast?
A forecast, on the other hand, predicts where your business is actually headed. It uses historical and current information to predict future financial outcomes. Forecasting allows management to see trends, adapt to changing market conditions, and adjust plans dynamically.
Unlike budgeting, forecasting activities are updated monthly or quarterly, ensuring decisions remain relevant to current market conditions and business environment.
Financial Budgeting and Forecasting ensures that forecasts stay aligned with corporate objectives and operational realities.
| Element | Budget | Forecast |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Plan targets | Predict outcomes |
| Timeframe | Fixed (annual) | Dynamic (monthly/quarterly) |
| Data Used | Historical | Historical + Real-time |
| Adjustments | Rare | Frequent |
| Example | Plan $500k profit | Expect $420k actual profit |
Key Differences Between Budgeting and Forecasting
The key differences between budgeting vs forecasting lie in their purpose, frequency, and flexibility. While budgeting sets a target, forecasting adapts it. Budgets provide financial objectives, but forecasts test how close a business is to achieving them.
A budget is based on past assumptions, while a forecast incorporates real-time data and a range of possible outcomes to better reflect changing business conditions.
In short, the differences between budgeting and forecasting can be summarized as:
- Budgeting sets the plan; forecasting refines it.
- Budget motivates performance; forecast measures actual performance.
- Budgets are rigid; forecasts evolve with business conditions change.
The Role of FP&A and Finance Teams
Within modern organizations, FP&A teams (Financial Planning and Analysis) and finance teams rely on both budgeting and forecasting to guide financial planning and shape the planning and budgeting process.
They compare actual results against the budget to calculate variance, helping management improve performance management and evaluate financial performance. This process helps in aligning financial goals with operational execution.
Using Data and Tools to Enhance Accuracy
The secret to reliable forecasting lies in data sources and financial modeling. Finance professionals use historical data to predict future trends and employ forecast in Excel models for quick insights. However, spreadsheets can cause version control issues, delays, and inconsistencies.
Modern budgeting and forecasting software and planning platforms now integrate real-time analytics, allowing teams to work from a single source of truth. This automation helps companies streamline updates and manage continuous planning as business conditions change.
Mini Case Study
A mid-sized retailer once relied entirely on Excel for forecasting. Due to version control issues and late updates, they missed key inventory signals, leading to overstock. After switching to software solutions offering real-time data, their forecast accuracy improved by 32%, and their time to value dropped by half.
Integrating Forecasting Into Financial Planning
Forecasting isn’t just about numbers — it’s about preparing for uncertainty. A good financial forecast uses data to predict future sales, costs, and profitability. It helps companies adapt plans and budgets to changing business conditions, ensuring agility in decision-making.
When financial documents like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow projections align with the forecasting process, the company gains clarity into future financial realities and accurate predictions.
Best Practices for Budgeting and Forecasting
1. Use Historical Data Effectively
Combine historical data with current market conditions to make accurate financial assumptions.
2. Adopt Continuous Planning
Leverage continuous planning methods like rolling forecasts to stay agile as changing business dynamics evolve.
3. Enhance Collaboration
Engage every stakeholder during the budget process to ensure ownership and accuracy.
4. Leverage FP&A Tools
Modern planning and forecasting tools eliminate spreadsheet dependency, supporting detailed financial reporting and faster updates.
5. Connect Budgeting With Strategy
The planning and budgeting process should always align with financial objectives and long-term financial strategies.
Practical Takeaways
- Combine your budget (the target) with your forecast (the reality).
- Review your financial statements regularly to compare actual performance.
- Use data-driven systems for performance management and forecasting.
- Maintain agility through continuous planning.
- Keep financial data centralized to ensure your team works from a single source of truth.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between budget and forecast can transform how a business operates. A budget lays out your ambition; a forecast helps you stay honest about your progress. The blend of both empowers finance teams to adapt swiftly to changing market conditions and improve accuracy in financial planning and analysis.
In a world where business conditions change overnight, combining smart tools with disciplined budgeting and forecasting ensures stability, foresight, and success. The next time you review your numbers, remember — your budget is your promise, but your forecast is your proof.
Start now — improve your financial strategy, master your numbers, and lead with clarity.
FAQs
What is the main difference between budget and forecast?
The difference between budget and forecast is that a budget sets fixed goals for spending and revenue, while a forecast continuously updates those expectations based on current market conditions.
How often should forecasts be updated?
Most companies update forecasts monthly or quarterly, depending on how fast their business conditions change.
Why is forecasting important in financial planning?
A financial forecast helps businesses predict future performance and adjust strategies to meet financial goals efficiently.
What are some best practices in budgeting and forecasting?
Effective budgeting and forecasting requires using real-time data, avoiding spreadsheet limitations, and engaging key stakeholders during the planning phase.
What tools can improve budgeting and forecasting accuracy?
Modern budgeting and forecasting software offers automation, real-time data, and collaboration features that simplify forecasting activities and the overall planning process.

